Section 3: Work

Work is the transfer of energy that occurs when a force makes an object move. For work to be done, something has to move, and the motion must be in the same direction as the force. For example, if you push a wheelbarrow and it does not move, then you haven’t done any work. When work is done, energy transfer from one object to another always occurs.
To calculate work, you multiply the applied force by the distance traveled. 
The rate at which work is done or energy is transferred is called power. So, for example, when you run a mile, you are using more power than you would if you were walking that mile because you’ve gone the same distance in less time.
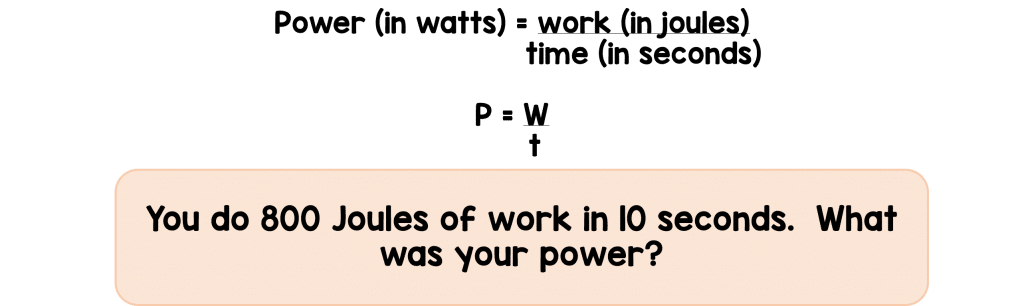
Review:
- Define work.
- Identify the formula used to calculate work.
- Identify the formula used to calculate power.
