Section 2: Cellular Respiration
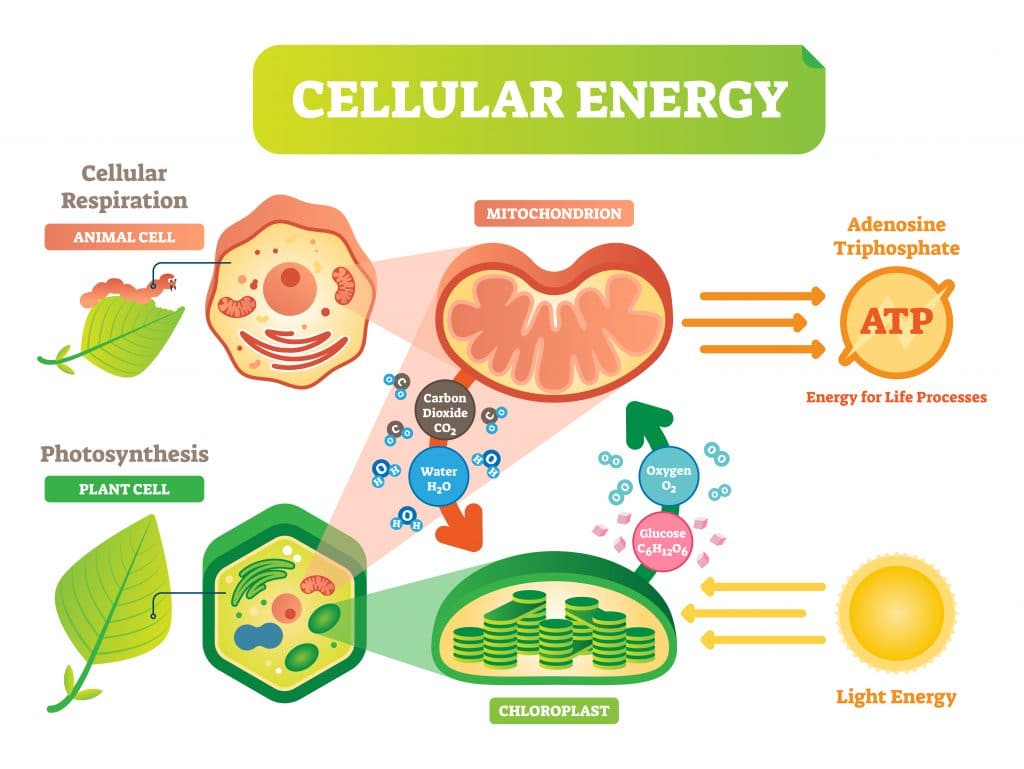
 Cellular respiration is the opposite of photosynthesis. Cellular respiration is the process by which cells obtain energy from glucose by breaking down simple food molecules such as sugar and releasing the stored energy. As a result, the energy in food is turned into energy the body can use.
Cellular respiration is the opposite of photosynthesis. Cellular respiration is the process by which cells obtain energy from glucose by breaking down simple food molecules such as sugar and releasing the stored energy. As a result, the energy in food is turned into energy the body can use.

There are two stages of cellular respiration. In stage one, the glucose is broken down into smaller molecules in the cytoplasm. Oxygen is not involved, and very little energy is released. Stage two takes place in the mitochondria. Molecules are broken down even further by chemical reactions. These chemical reactions require oxygen and release a great deal of energy. In addition, carbon dioxide and water are released. In most animals, these two products are released by exhaling.
Photosynthesis releases oxygen into the atmosphere, and cellular respiration uses that oxygen to release energy stored in food. Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the air, and cellular respiration returns it.
Fermentation is a way of providing energy to cells without using oxygen. For example, alcoholic fermentation is used in winemaking and baking. Another common fermentation type is lactic acid, which is felt in the muscles after extreme exertion.
Review:
- How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration different?
- What is the role of mitochondria in cellular respiration?
- Identify two types of fermentation.
