Section 5: Changes in States of Matter
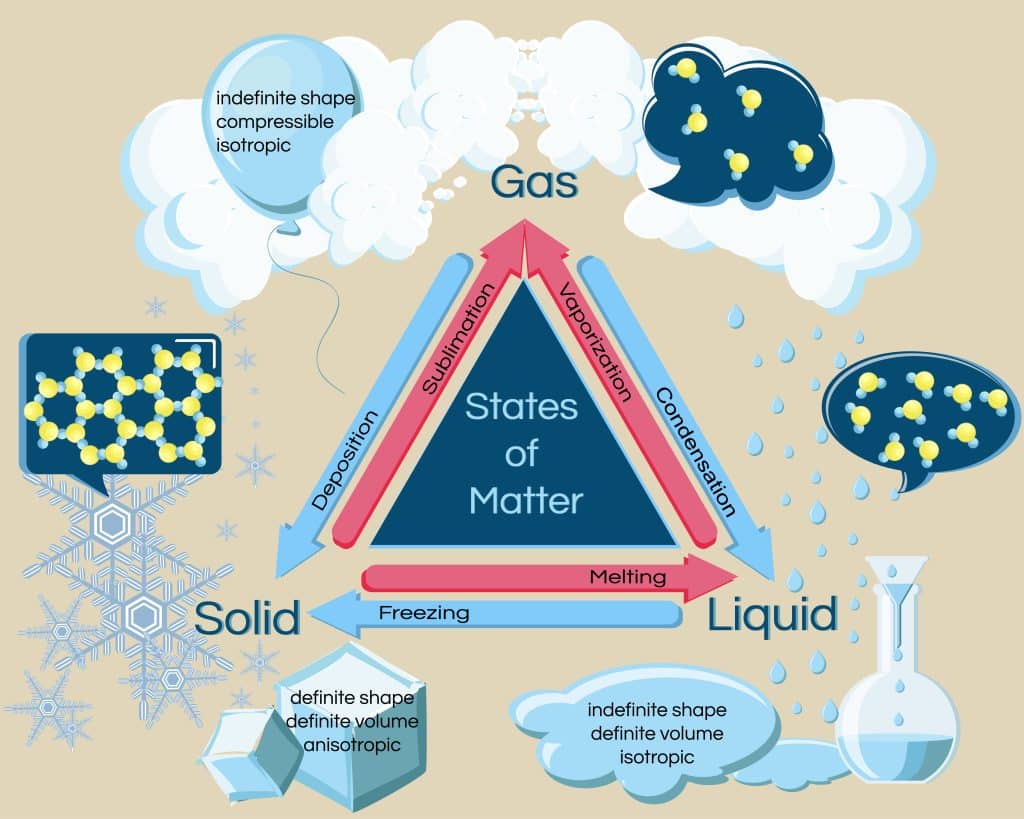
Matter often changes. When enough heat is added to a liquid, it will begin to boil and turn into a gas. The bubbles are water vapor, and as more heat is added, the bubbles become larger and larger. The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which the liquid begins to vaporize. The added heat gives the molecules in the liquid more kinetic energy. Vaporization is the change from a liquid state to a gaseous state. Vaporization can be used to describe both boiling and evaporation. Evaporation is vaporization that occurs only at the surface of a liquid. It can occur at temperatures below the liquid’s boiling point. For example, if you leave a cup of water unattended on the counter, the water will eventually evaporate.
When something melts, it changes from a solid state to a liquid state. The melting point is the temperature at which a solid melts. When something freezes, it changes from a liquid state to a solid state. The freezing point is the temperature at which a liquid freezes. Condensation occurs when there is a change from a gaseous state to a liquid state. The condensation point is the temperature at which gas condenses.
Review:
- What is boiling point?
- When does condensation occur?
- Explain evaporation.
